
How Lipid Disorders Affect Your Heart Health and How to Prevent Them

Dr. W. Rizvi
5 Feb 2025
Lipid Disorders and Their Impact on Cardiovascular Health
Lipid disorders are called dyslipidemia, which occurs when irregular fats (lipids) are in the bloodstream. These fats, including cholesterol and triglycerides, play important roles in the body, such as building cell membranes and producing hormones. However, when these levels become too high or too low, it can lead to many serious health issues, particularly affecting the heart and blood vessels. Lipid disorders typically don't show symptoms right away, but over time, they can significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) like heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. “With cardiovascular disease being the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, effective and cost-efficient therapies to reduce cardiovascular risk are highly needed. Lipids and lipoprotein particles crucially contribute to atherosclerosis as an underlying pathology of cardiovascular disease and influence inflammatory processes as well as the function of leukocytes vascular and cardiac cells, thereby impacting vessels and the heart.”
Different Types of Lipid Disorders
There are several types of lipid disorders, each with its own set of implications for heart health:
- High Cholesterol (Hypercholesterolemia): This condition is usually caused by an excess of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), which is often called "bad" cholesterol. High levels of LDL lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, which thickens and narrows the arteries—a process known as atherosclerosis. This restricts blood flow and can ultimately lead to a heart attack or stroke.
- Low High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): HDL is the "good" cholesterol because it helps clear excess LDL from the bloodstream. When HDL levels are low, the body becomes less operative at removing harmful cholesterol, raising the risk of heart disease.
- High Triglycerides: Triglycerides are another form of fat found in the blood. Elevated triglyceride levels often coincide with high LDL and low HDL, further increasing the risk of heart disease. High triglyceride levels also hold the blame for increasing the risk of inflammation of the pancreas.
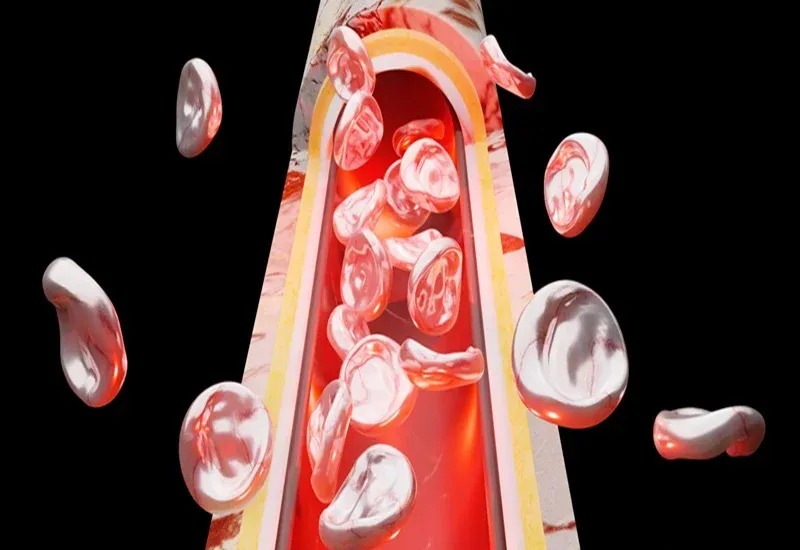
Cholesterol and Its Role in Heart Health
Cholesterol is essential for the body's functions, but having too much of the wrong cholesterol can harm heart health. There are two key types of cholesterol:
- LDL Cholesterol: is "bad" cholesterol because it contributes to plaque buildup in the arteries, blocks blood flow, and increases the risks of heart attacks and strokes.
- HDL Cholesterol: is the "good" cholesterol that helps clear LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream, protecting the arteries from damage and preventing plaque buildup.
- Triglycerides: Elevated triglyceride levels can also have a very bad impact on heart health, contributing to high blood pressure and also increase the risk of developing diabetes.
How to Manage Cholesterol and Protect Your Heart
A balance of cholesterol is vital for heart health. Several practical steps can help improve overall heart health by managing cholesterol levels.
1. Adopting a Heart-Healthy Diet
Eating a well-balanced, heart-healthy diet is one of the best ways to control cholesterol levels. Some dietary tips include:
- Cutting down on unhealthy fats: Avoid foods whole of saturated fats and trans fats, such as fried foods, processed meats, and packaged snacks, which contribute to elevated LDL cholesterol.
- Increasing healthy fats: Instead, focus on eating more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which help raise HDL cholesterol. Foods like avocados, olives, and fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, and sardines) are good choices.
- Boosting fiber intake: Foods high in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, apples, and carrots, help lower LDL cholesterol by tying it and removing it from the body.
- Focusing on plant-based foods: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce cardiovascular risk.
2. Getting Active
Regular physical activity improves cholesterol levels, such as cycling, walking, and exercise. Exercise can raise HDL cholesterol while lowering LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
Being overweight or obese can negatively affect cholesterol levels. Excess weight loss through a combination of healthy eating and regular exercise can help bring your lipid levels back into a healthier range.
3. Quitting smoking
Smoking has multiple harmful effects on heart health, one of which is lowering HDL cholesterol. Smoking also damages blood vessels and builds up plaque in the arteries. Quitting smoking can improve cholesterol levels and greatly reduce the risk of heart disease.

Need any help?
Contact us4. Managing Stress
Chronic Stress can negatively affect cholesterol levels by contributing to unhealthy habits like overeating or a lack of physical activity. Stress management techniques, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can positively impact on your physical and mental health, helping you manage cholesterol and reduce heart disease risk.
5. Regular Health Check-Ups
Routine check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring cholesterol and lipid levels. Regular testing through lipid panels can detect any imbalances sooner, allowing for timely intervention through lifestyle changes or medications if needed.
Preventing Lipid Disorders
The best way to prevent lipid disorders is to adopt healthy lifestyle habits that help keep cholesterol and triglyceride levels within a normal range. Here's how to do it:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet: Focus on a diet low in unhealthy fats and high in fiber and healthy fats from plant-based sources.
- Exercise regularly: Get at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week to keep cholesterol levels in balance.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of lipid imbalances and associated diseases.
- Quit smoking: Stopping smoking can help raise HDL cholesterol and protect blood vessels.
- Practice stress management: Reduce the negative effects of stress through relaxation techniques and physical activity.
- Get regular check-ups: Regularly monitor your cholesterol levels with the help of your healthcare provider.
Individuals who have a genetic predisposition to lipid disorders or are at high risk and may need medications like statins or fibrates to manage their cholesterol levels.
Contact your Endocrinologist today, Dr. W. Rizvi at R-endocrinology, to learn more about how lipid disorder affect your heart health and how to prevent them.
Resource:
Share This:
Disclaimer
*Please note that the information provided in the blogs and articles is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. We strive to bring you the latest information about the endocrine world; however, we encourage you to seek individual medical advice and treatment options during your consultation with a qualified healthcare professional. *
